Javascript Gauge Style Range Control With SVG
Submitted by rinvizle on Wednesday, August 31, 2016 - 15:55.
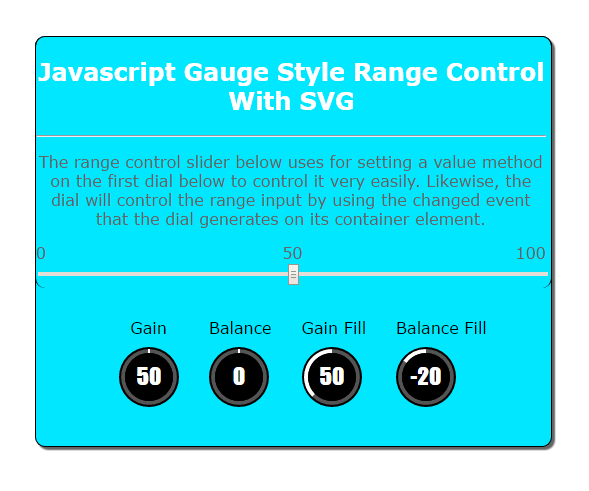
This tutorial will show you have to create a Gauge Application using Javascript. Javascript Gauge Style Range Control With SVG application is a handy JavaScript plugin for generating and animating nice and clean gauges and it has a dial and svg component to be rendered within any browsers. Gauge application that has a Javascript plugin is visualize to any values into touchable, customizable, vector shaped and gauge-style dial graph or a great alternative to default range input. See the example code below.
Index Javascript script - this is for the calling of the data in every id's to call and creating a value for each gauge.
For the CSS - this css is for the creating of the design or to make it more responsive to the user's eyes.
Hope that you learn from this tutorial and don't forget to Like & Share. Enjoy Coding!
Sample Code
Index.html - this is for the main page of the system for displaying the data through html.- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <link rel="stylesheet" media="all" href="Gauge/gauge.min.css">
- <link rel="stylesheet" media="all" href="Gauge/gaugestyle.css">
- </head>
- <body>
- <div class="content">
- <div class="form">
- <div class="slider">
- <p align="center">The range control slider below uses for setting a value method on the first dial below to control it very easily. Likewise, the dial
- will control the range input by using the changed event that the dial generates on its container element.</p>
- <div class="slider-labels">0                      
-                    50<span>100</span></div>
- <input id="slider-example" type="range" min="0" max="100"/>
- </div>
- </div>
- <div class="pgauge">
- <div class="panel">
- <span>  Gain</span>
- <div id="gain" class="gauge"></div>
- </div>
- <div class="panel">
- <span>Balance </span>
- <div id="balance" class="gauge"></div>
- </div>
- <div class="panel">
- <span>Gain Fill</span>
- <div id="gain-fill" class="gauge"></div>
- </div>
- <div class="panel">
- <span>Balance Fill</span>
- <div id="balance-fill" class="gauge"></div>
- </div>
- </div>
- </div>
- </body>
- </html>
- var gainNotch = document.querySelector('#gain');
- var balanceNotch = document.querySelector('#balance');
- var gainFill = document.querySelector('#gain-fill');
- var balanceFill = document.querySelector('#balance-fill');
- var gainNotchDial = new Gauge(gainNotch);
- var balanceNotchDial = new Gauge(balanceNotch, {type:'balance',display:'notch',min:-50,max:50,value:0});
- var gainFillDial = new Gauge(gainFill, {type:'gain',display:'fill'});
- var balanceFillDial = new Gauge(balanceFill, {type:'balance',display:'fill',min:-50,max:50,value:-20,inputId:'unique-id'});
- var rangeInput = document.querySelector('#slider-example');
- rangeInput.addEventListener('input', function(e)
- {
- gainNotchDial.setValue(this.value);
- }, true);
- gainNotch.addEventListener('changed', function(e)
- {
- rangeInput.value = e.detail;
- });
- gainNotchDial.addEventListener('changed', function(e)
- {
- console.log('Gauge event triggered with object: ' + JSON.stringify(e));
- });
- body {
- font-family:Verdana;}
- .content {
- margin-left:500px;
- margin-top: 100px;
- width:515px;
- height: 410px;
- border-bottom:solid 1px;
- border-left:solid 1px;
- border-right:solid 1px;
- background-color:#00e7ff;
- border-radius:10px;
- box-shadow: 3px 3px 1px rgba(50, 50, 50, 0.75);
- }
- .form {
- margin-left:-1px;
- width:515px;
- border-top:solid 1px;
- border-left:solid 1px;
- border-right:solid 1px;
- border-radius: 10px;
- }
- h2 {
- color:#fff;
- }
- h3 {
- color:#ffff;
- }
- .panel {
- float:left;
- padding:15px;
- background-color:#00e7ff;
- }
- .gauge {
- width:60px;
- height:60px;
- margin-top:10px;
- }
- .pgauge {
- margin-left:68px;
- position:fixed;
- }
- .slider {
- width:510px;
- margin:15px 0;
- color:#666666;
- }
- .slider input {
- width:100%;
- }
- .slider .slider-labels span {
- float:right;
- }
- p {
- margin:15px 0;
- width:510px;
- color:#666666;
- }
- #gain-notch svg circle.value-background {
- background-color:blue;
- }
- #style-4 svg circle.value-background {
- fill:white;
- }
Add new comment
- 103 views